Top Tips Of Renewal 1Z0-821 Exam
Proper study guides for Up to the minute Oracle Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator certified begins with Oracle 1Z0-821 preparation products which designed to deliver the Vivid 1Z0-821 questions by making you pass the 1Z0-821 test at your first time. Try the free 1Z0-821 demo right now.
Free demo questions for Oracle 1Z0-821 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
Your mentor suggests using the dladm rename-link command to rename the network datalinks.
What are the two advantages of following this advice?
- A. It can clarify which network interface has what purpose.
- B. It can simplify specifying the network interface with the dladm modify-aggr command.
- C. It can simplify specifying the network interface with the dladm modify-bridge command.
- D. It can simplify IP filter rule changes if the network interface is replaced with a different type.
- E. It can prevent accidental deletion of the network interface with the dladm delete-phys command.
- F. It can prevent accidental deletion of the network interface configuration with the ipadm delete-addr command.
Answer: AD
Explanation:
Note: dladm rename-link [-R root-dir] link new-link
Rename link to new-link. This is used to give a link a meaningful name, or to associate existing link configuration such as link properties of a removed device with a new device.
NEW QUESTION 2
Review the storage pool information:
Choose the correct procedure to repair this storage pool.
- A. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- B. When the system is booted, execute the zpool clear pool1 command.
- C. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- D. When the system is booted execute the zpool online pool1 command.
- E. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- F. When the system is booted, execute the zpool replace pool1 c3t3d0 command.
- G. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- H. When the system is booted, execute the zpool replace pool1 c3t3d0 c3t3d0 command.
Answer: C
Explanation:
You might need to replace a disk in the root pool for the following reasons: The root pool is too small and you want to replace it with a larger disk
The root pool disk is failing. In a non-redundant pool, if the disk is failing so that the system won't boot, you'll need to boot from an alternate media, such as a CD or the network, before you replace the root pool disk.
In a mirrored root pool configuration, you might be able to attempt a disk replacement without having to boot from alternate media. You can replace a failed disk by using the zpool replace command.
Some hardware requires that you offline and unconfigure a disk before attempting the zpool replace operation to replace a failed disk.
For example:
# zpool offline rpool c1t0d0s0
# cfgadm -c unconfigure c1::dsk/c1t0d0
<Physically remove failed disk c1t0d0>
<Physically insert replacement disk c1t0d0>
# cfgadm -c configure c1::dsk/c1t0d0
# zpool replace rpool c1t0d0s0
# zpool online rpool c1t0d0s0
# zpool status rpool
<Let disk resilver before installing the boot blocks>
SPARC# installboot -F zfs /usr/platform/`uname -i`/lib/fs/zfs/bootblk /dev/rdsk/c1t0d0s0 x86# installgrub /boot/grub/stage1 /boot/grub/stage2 /dev/rdsk/c1t9d0s0
NEW QUESTION 3
Identify three differences between the shutdown and init commands.
- A. Only shutdown broadcasts a final shutdown warning to all logged-in users.
- B. init does not terminate all services normall
- C. The shutdown command performs a cleaner shutdown of all services.
- D. The shutdown command can only bring the system to the single-user mileston
- E. The init command must be used to shut the system down to run level 0.
- F. Only shutdown sends a shutdown message to any systems that are mounting resources from the system that is being shut down.
- G. The shutdown command will shut the system down and turn off power; init will only shut the system down.
Answer: ABE
NEW QUESTION 4
Identify the correctly matching pair of equivalent functionality of JumpStart and Automated installer (AI).
- A. JumpStart: begin script AI: package repository
- B. JumpStart: setup_serverAI: installadm create-service
- C. JumpStart: add_Install_clientAI: SMF system configuration profile files
- D. JumpStart: finish scripts and sysidsfg filesAI: manifest files
Answer: B
Explanation:
JumpStart: Use the setup_install_server(1M) command. AI: Use the installadm create-service command.
NEW QUESTION 5
You are the administrator for a group of shell script developers. They use vi, and have asked you to make their scripts automatically executable when they save their files.
How can this be accomplished?
- A. Enter set –o vi on the command line, or include it in each user's startup script.
- B. Enter umask –s on the command line, or include it in each user's startup script.
- C. Enter umask 000 on the command line, or include it in each user's startup script.
- D. Enter umask 777 on the command line, or include it in each user's startup script.
- E. It is not possible to automatically set the execute bit on with the umask setting, or vi option.
- F. Enter umask 766 the command line, or include it in the global startup script for the default shell.
Answer: E
Explanation:
Unlike DOS, which uses the file extension to determine if a file is executable or not, UNIX relies on file permissions.
The value assigned by umask is subtracted from the default.
User's file creation mask. umask sets an environment variable which automatically sets file permissions on newly created files. i.e. it will set the shell process's file creation mask to mode.
umask 000 would grant full permissions. Note: 777 full permissions
NEW QUESTION 6
The /usr/bin/p7zip file that is part of the p7zip package has been overwritten. This server is critical to production and cannot be rebooted. Identify the command that would restore the file without requiring a reboot.
- A. pkg verify p7zip
- B. pkg fix p7sip
- C. pkg rebuild-index p7zip
- D. pkg revert p7zip
- E. pkg uninstsll p7zip
- F. pkg install p7zip
- G. pkg install --no-backup-be p7sip
- H. pkg refresh p7zip
Answer: D
Explanation:
Use the pkg revert command to restore files to their as-delivered condition.
NEW QUESTION 7
You are installing the Solaris 11 Operation System by using the Text Installer. A panel
prompts you to create a root password and a user account.
Which four describe your options for completing this panel of the Installation?
- A. Creating a user account is optional.
- B. The root password must be set and cannot be blank.
- C. The root password can be left blank.
- D. If you provide a username, that user is assigned the root role.
- E. If you provide a username, that user is given root privileges.
- F. If you provide a username, root is an account rather than a role and is set to expire immediately.
- G. If you do not provide a username, root is an account rather than a role and is set to expire immediately.
Answer: ABDG
Explanation:
A: You are not required to create a user account. B: You must create a root password.
D: If you create a user account in this panel, you need to provide both the user's password and a root password.
In this case, root will be a role assigned to the user.
G: If you do not create a user account, you still need to provide a root password. In this case, root will be a regular user.
NEW QUESTION 8
You need to connect two nonglobal zones using a private virtual network. Identify the network resources required in the global zone to accomplish this.
- A. an etherstub and two virtual network interfaces
- B. a virtual bridge
- C. two virtual network interfaces.
- D. two etherstubs
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 9
You have been asked to do an orderly shutdown on a process with a PID of 1234, with the kill command.
Which command is best?
- A. kill -2 1234
- B. kill -15 1234
- C. kill -9 1234
- D. kill -1 1234
Answer: B
Explanation:
On POSIX-compliant platforms, SIGTERM is the signal sent to a process to request its termination. The symbolic constant for SIGTERM is defined in the header file signal.h. Symbolic signal names are used because signal numbers can vary across platforms, however on the vast majority of systems, SIGTERM is signal #15.
SIGTERM is the default signal sent to a process by the kill or killall commands. It causes the termination of a process, but unlike the SIGKILL signal, it can be caught and interpreted (or ignored) by the process. Therefore, SIGTERM is akin to asking a process to terminate nicely, allowing cleanup and closure of files. For this reason, on many Unix systems during shutdown, init issues SIGTERM to all processes that are not essential to powering off, waits a few seconds, and then issues SIGKILL to forcibly terminate any such processes that remain.
NEW QUESTION 10
User brian changes the permissions for db_data this command: chmod 4755 db_data
What is true?
- A. db_data now has permissions rwsr-xr-x and can be deleted only by user brian.
- B. db_data now has permissions rwsr-xr-x and, if executed, will inn with the permissions of user brian.
- C. db_data now has permissions rwxr-sr-x and can be deleted only by members of the group owning it.
- D. The permissions for db_data cannot be determined, because the permissions prior to the change have not been specified.
- E. db_data must be an ordinary file, because special permissions cannot be set on a directory.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Use the chmod command to change permissions for a file or directory. You must be the owner of a file or directory, or have root access, to change its permissions.
Here we do not know if brian owns db_data. Note:
Permission 7 full
6 read and write
5 read and execute 4 read only
3 write and execute 2 write only
1 execute only
0 none
0 --- no permission 1 --x execute
2 -w- write
3 -wx write and execute 4 r-- read
5 r-x read and execute 6 rw- read and write
7 rwx read, write and execut
Solaris: Solaris Advanced User's Guide
NEW QUESTION 11
Your server has one zone named dbzone (hat has been configured, but not yet installed). Which command would you use to view all the options that were used to configure this zone?
- A. zoneadm list –icv dbzone
- B. zones tat –c summary dbzone
- C. zonecfg –z dbzone info
- D. zonecfg –icv dbzone info
Answer: C
Explanation:
zonecfg info
Display information about the current configuration. If resource-type is specified, displays only information about resources of the relevant type. If any property-name value pairs are specified, displays only information about resources meeting the given criteria. In the resource scope, any arguments are ignored, and info displays information about the resource which is currently being added or modified.
Note: zonecfg –z
zonename. Specify the name of a zone. Zone names are case sensitive. Zone names must begin with an alphanumeric character and can contain alphanumeric characters, the underscore (_) the hyphen (-), and the dot (.). The name global and all names beginning with SUNW are reserved and cannot be used.
Incorrect Answer
A: The zoneadm utility is used to administer system zones. A zone is an application container that is maintained by the operating system runtime.
list option:
Display the name of the current zones, or the specified zone if indicated. B: No such command.
D: no such options zonecfg –icv
NEW QUESTION 12
A datalink can best be described as .
- A. a driver for a Network Interface Card
- B. the software connecting the Internet Layer and the Physical Layer
- C. a device that provides Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- D. a logical object used for IP Multipathing
Answer: D
Explanation:
The command dladm is used to configure data-link interfaces in Sun Solaris. A configured data-link is represented in the system as interface that can be used for TCP/IP. Each data- link relies on either a single network device or an link aggregation device to send & recieve packets.
Network interfaces provide the connection between the system and the network. These interfaces are configured over data links, which in turn correspond to instances of hardware devices in the system.
In the current model of the network stack, interfaces and links on the software layer build on the devices in the hardware layer. More specifically, a hardware device instance in the
hardware layer has a corresponding link on the data-link layer and a configured interface on the interface layer. This one-to-one relationship among the network device, its data link, and the IP interface is illustrated in the figure that follows.
Network Stack Showing Network Devices, Links, and Interfaces: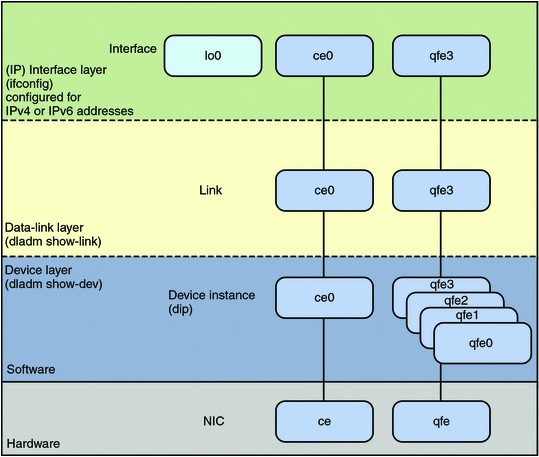
NEW QUESTION 13
You are creating a non-global zone on your system.
Which option assigns a zpool to a non-global zone, and gives the zone administrator permission to create zfs file system in that zpool?
- A. While creating the non-global zone, make the following entry: add deviceset match=/dev/rdsk/c4t0d0endBoot the zone and log in the zone as roo
- B. Create the zpool: zpool create pool2 c4t0d0In the non-global zone, root can now create ZFS file system in the pool2 zpool
- C. In the global zone, create the zpool: global# zpool create pool2 c4t1d0While creating the no-global zone, make the following entry: add datasetset name=pool2endadd fsset dir=pool1set special=pool1set type=zfspool1endBoot the zone, log in the zone as root, and create the zfs file system in the pool2 zpool.
- D. In the global zone, create the zpool:global#zpool create pool2 c4t1d0While creating the global zone, make the following entry: add datasetset name=pool2endBoot the zone, log in to the zone as root and create the zfs file systems in the pool2 zpool.
- E. In the global zone, create the zpool and the ZFS file systems that you want to use in the non-global zone: global#zpool create pool2 c4t1d0global#zfs create pool2/dataWhile creating the non-global zone, make the following entry for each ZFS file system that you want to make available in the zone: add fsset dir=/dataset special=pool2/dataset type=zfsend
- F. Create the zpool in the global zone: global#zpool create pool2 c4t1d0Boot the non- global zone, log in to the zone as root, and issue this command to delegate ZFS permissions to root: non-global zone# zfs allow root create , destroy, mount pool2Log in to the non-global zone create ZFS file systems in the pool2 zpool.
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19253-01/819-5461/gbbst/index.html
NEW QUESTION 14
Which three of the components could be used in a ZFS storage pool, but are not recommended configurations?
- A. A file on a UFS file system
- B. A Veritas Volume Manager (VxVM) volume
- C. A LUN In a hardware RAID array
- D. A disk slice from an SMI labeled disk
- E. A Solaris Volume Manager (SVM) volume
- F. An EFI labeled disk
Answer: ABE
Explanation:
A: ZFS also allows you to use UFS files as virtual devices in your storage pool. This feature is aimed primarily at testing and enabling simple experimentation, not for production use. The reason is that any use of files relies on the underlying file system for consistency. If you create a ZFS pool backed by files on a UFS file system, then you are implicitly relying on UFS to guarantee correctness and synchronous semantics.
However, files can be quite useful when you are first trying out ZFS or experimenting with more complicated layouts when not enough physical devices are present. All files must be specified as complete paths and must be at least 64 Mbytes in size.
B, E: You can construct logical devices for ZFS using volumes presented by software-
based volume managers, such as Solaris Volume Manager (SVM) or Veritas Volume Manager (VxVM). However, these configurations are not recommended. While ZFS functions properly on such devices, less-than-optimal performance might be the result.
NEW QUESTION 15
User jack logs in to host solaris and then attempts to log in to host oracle using ssh. He receives the following error message:
The authenticity of host oracle (192.168.1.22) can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 3B:23:a5:6d:ad:a5:76:83:9c:c3:c4:55:a5:18:98:a6
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
Which two are true?
- A. The public host key supplied by solaria is not known to the host oracle.
- B. The error would not occur if the RSA key fingerprint shown in the error message was added to the /etc/ssh/known_hosts file on solaris.
- C. The private host key supplied by oracle is not known to solaris.
- D. If jack answers yes, the RSA public key for the host oracle will be added to the known_hosts file for the user jack.
- E. The public host key supplied by oracle is not known to the host solaris.
Answer: BD
Explanation:
The fingerprints are used to guard against man in the middle attacks. Since ssh logins usually work over the internet (an insecure connection), someone could hijack your connection. When you try to log into yourmachine.com, he could get "in the middle" and return your challenge as if he was yourmachine.com. That way, he could get hold of your login password.
To make this attack harder, ssh stores the fingerprint of the server's public key on the first connection attempt. You will see a prompt like:
The authenticity of host 'eisen (137.43.366.64)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is cf:55:30:31:7f:f0:c4:a0:9a:02:1d:1c:41:cf:63:cf. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)
When you enter yes, ssh will add the fingerprint to your known_hosts file. you will see
Code:
Warning: Permanently added 'eisen, 137.43.366.64' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
The next time you login, ssh will check whether the host key has changed. A changing host key usually indicates a man in the middle attack, and ssh refuses to connect.
NEW QUESTION 16
You have installed the SMF notification framework to monitor services. Which command is used to set up the notifications for a particular service?
- A. svccfg
- B. svcadm
- C. setnotify
- D. smtp-notify
Answer: A
Explanation:
How to Set Up Email Notification of SMF Transition Events
This procedure causes the system to generate an email notification each time one of the services or a selected service has a change in state. You can choose to use either SMTP or SNMP. Normally, you would only select SNMP if you already have SNMP configured for some other reason.
By default, SNMP traps are sent on maintenance transitions. If you use SNMP for monitoring, you can configure additional traps for other state transitions.
1. Become an administrator or assume a role that includes the Service Management rights profile.'
2. Set notification parameters. Example 1:
The following command creates a notification that sends email when transactions go into the maintenance state.
# /usr/sbin/svccfg setnotify -g maintenance mailto:sysadmins@example.com
Example 2:
The following command creates a notification that sends email when the switch service goes into the online state.
# /usr/sbin/svccfg -s svc:/system/name-service/switch:default setnotify to-online \ mailto:sysadmins@example.com
Note: The svccfg command manipulates data in the service configuration repository. svccfg can be invoked interactively, with an individual subcommand, or by specifying a command file that contains a series of subcommands.
Changes made to an existing service in the repository typically do not take effect for that service until the next time the service instance is refreshed.
NEW QUESTION 17
Server A, Server B, and Server C are connected to the same network switch and are on the sari Each server has a single network interface, net0.
You received a tech support call that Server B has lost network connectivity. Your troubleshooting has discovered:
Server A can ping Server C, but not Server B. Server B can ping localhost, but not Server A or C. Server C can ping Server A, but not Server B.
On Server F3, you enter the following command: dladm show-phys | grep net0
Response:
net0/v4 Ethernet down 0 unknown el00gl
What is the next logical troubleshooting action?
- A. Run arp -a on all servers.
- B. Confirm that the router is working.
- C. Confirm that the power light of the network switch is on.
- D. Confirm that the physical network connections are intact.
- E. On Server A and C, run tranceroute –n server.
- F. On Server B, run tranceroute –n servera and tranceroute –n serverc.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Check the physical connection.
NEW QUESTION 18
A user brian is configured to use the bash shell. His home directory is /export/home/brian, and contains a .profile and a .bashrc file.
In the -profile, there are these lines: genius =ritchie
export genius
In the .bashrc us this line: genius=kernighan
In /etc/profile are these lines: genius=thompson
export genius
When brian logs in and asks for the value of genius, what will he find, and why?
- A. genius will be ritchie, because that was the value exported in .profile.
- B. genius will be kernighan, because .bashrc executes after .profile.
- C. genius will be ritchie because variable settings in .profile take precedence over variable settings in .bashrc.
- D. genius will be ritchie because .profile executes after .bashrc.
- E. genius will be thompson because /etc/profile system settings always override local settings.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 19
The storage pool configuration on your server is:
You back up the /pool1/data file system, creating a snapshot and copying that snapshot to tape (/dev/rmt/0). You perform a full backup on Sunday night and Incremental backups on Monday through Saturday night at 11:00 pm. Each incremental backup will copy only the data that has been modified since the Sunday backup was started.
On Thursday, at 10:00 am, you had a disk failure. You replaced the disk drive (c4t0d0). You created pool (pool1) on that disk.
Which option would you select to restore the data in the /pool1/data file system?
- A. zfs create pool1/dataLoad the Monday tape and enter:zfs recv pool1/data </dev/rmt/0Load the Wednesday tape and enter:zfs recv –F pool1/data < /dev/rmt/0
- B. Load the Sunday tape and restore the Sunday snapshot:zfs recv pooll/data </dev/rmt/0zfs rollback pool1/data@monLoad the Wednesday tape and restore the Wednesday snapshot:zfs recv –i pooll/data < /dev/rmt/0zfs rollback pool1/data@wed
- C. zfs create pooll/dataLoad the Wednesday tape and enter:zfs recv -F pool1/data </dev/rmt/0
- D. Load the Sunday tape and enter:zfs recv pool1/data < /dev/rmt/0Load the Wednesday tape and enter:* commands missing*
Answer: D
Explanation:
First the full backup must be restored. This would be the Sunday backup.
Then the last incremental backup must be restored. This would be the Wednesday backup. Before restoring the Wednesday incremental file system snapshot, the most recent snapshot must first be rolled back.
By exclusion D) would be best answer even though it is incomplete.
NEW QUESTION 20
You are installing Oracle Solaris 11 on a SPARC-based system by using the Test Installer. Which three statements are true?
- A. The ROOT user will always be configured as a role.
- B. The root filesystem will always be deployed on ZFS.
- C. The root filesystem will always be located on a local disk.
- D. The network can be configured using DHCP.
- E. The set of packages that will be installed are server based.
- F. You must always create one regular user when installing the system.
Answer: BDE
NEW QUESTION 21
Review the boot environment information displayed on your system:
Which two options accurately describe the newBE boot environment?
- A. It cannot be destroyed.
- B. It cannot be activated.
- C. It cannot be renamed.
- D. You can create a snapshot of it.
- E. It is activated but unbootable.
- F. It has been deleted and will be removed at the next reboot.
Answer: BC
Explanation:
If the boot environment is unbootable, it is marked with an exclamation point (!) in the
Active column in the beadm list output.
The beadm command restricts actions on unbootable boot environments as follows: You cannot activate an unbootable boot environment. (B)
You cannot destroy a boot environment that is both unbootable and marked as active on reboot.
You cannot create a snapshot of an unbootable boot environment.
You cannot use an unbootable boot environment or boot environment snapshot with the -e option of beadm create.
You cannot rename an unbootable boot environment. (C)
NEW QUESTION 22
......
Recommend!! Get the Full 1Z0-821 dumps in VCE and PDF From Thedumpscentre.com, Welcome to Download: https://www.thedumpscentre.com/1Z0-821-dumps/ (New 243 Q&As Version)